 |
 |
- Search
| Ann Child Neurol > Volume 31(4); 2023 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
Methods
Results
Conclusion
Notes
Author contribution
Conceptualization: ADPC and MAAMV. Formal analysis: ADPC. Methodology: ADPC and MAAMV. Writing-original draft: ADPC and MAAMV. Writing-review & editing: ADPC and MAAMV.
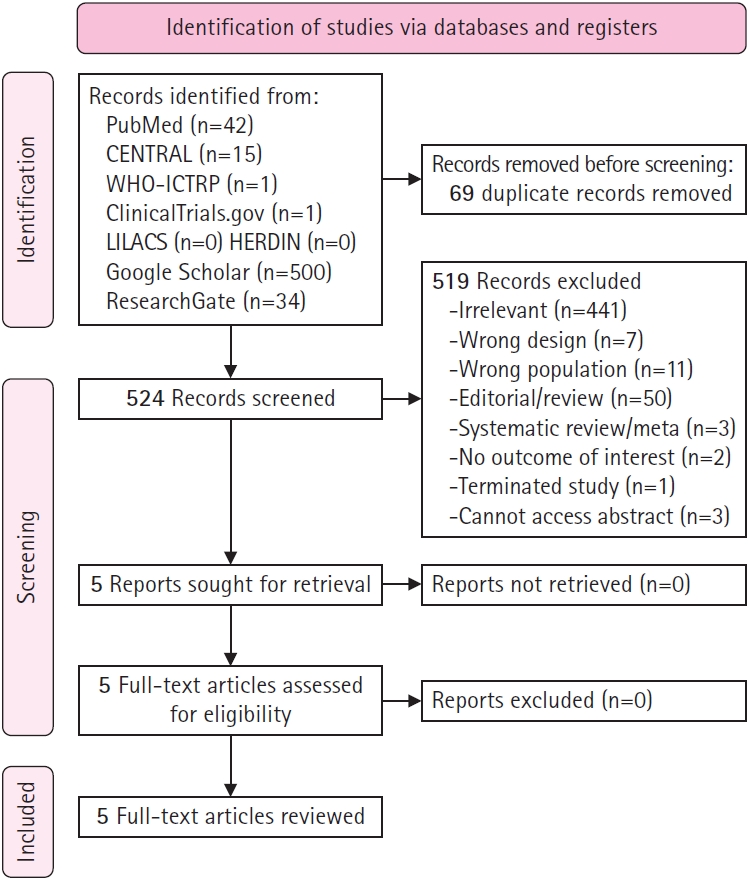
Fig.┬Ā1.
Table┬Ā1.
| Study/Country | Design/sample size | Mean age (yr)/% male | Mean baseline MAS | Mean baseline GMFM | Tizanidine dose | Treatment duration (wk) | Outcomes reported |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vasquez-Briceno et al. (2006) [14]/Mexico | RCT; n=40 (tizanidine, 10; control, 30) Control: placebo | 4.1 T: 30% C: 35% | NR | NR | 0.05 mg/kg/day | 24 | MAS, adverse events |
| Dai et al. (2008) [13]/Turkey | Retrospective cohort; n=30 (tizanidine, 13; control, 17) Control: baclofen | 5.6 T: 64% C: 69% | T: 3.69 C: 3.65 | T: 47.40 C: 46.04 | 0.3-0.5 mg/kg/day | 12 | MAS, GMFM, adverse events |
| Nikkhah et al. (2011) [15]/Iran | RCT; n=60 (tizanidine, 30; control, 30) Control: placebo | 7.3 52% | NR | NR | <7 years old: 2 mg/day >7 years old: 4 mg/day | 2 | MAS, pain reduction |
| Dai et al. (2016) [12]/Turkey | Retrospective cohort; n=64 (tizanidine, 33; control, 31) Control: baclofen | 4.9 T: 63% C: 64% | T: 3.79 C: 3.61 | T: 45.18 C: 44.14 | 0.3-0.5 mg/kg/day | 12 | MAS, GMFM, adverse events |
| Haque et al. (2020) [16]/Bangladesh | RCT; n=70 (tizanidine, 35; control, 35) Control: baclofen | 2.39 % Male: NR | NR | NR | Starting dose <10 years old: 2 mg Ōēź10 years old: 4 mg Maintenance dose after 1 week: 0.3 mg/kg/day | 24 | MAS, GMF classification system, adverse events |
Table┬Ā2.
| Study | Reduction in spasticity | Reduction in pain | Gross motor function after treatment | Adverse events |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vasquez-Briceno et al. (2006) [14]a Control: placebo | Mean improvement in MAS score was greater in the treatment group (78.85% vs. 7.644%, P=0.0001). | NR | NR | No adverse events. |
| Detailed % improvement per site: | All liver function tests were normal. | |||
| - Shoulder flexors: 93.9% vs. 8.8% | ||||
| - Elbow flexors: 88% vs. 8.3% | ||||
| - Hand flexors: 87% vs. 5.7% | ||||
| - Hip abduction: 59.2% vs. 8.9% | ||||
| - Hip flexors: 91.1% vs. 7.2% | ||||
| - Knee flexors: 83% vs. 6.8% | ||||
| - Foot dorsiflexion: 48.3% vs. 7.6% | ||||
| Dai et al. (2008) [13]b Control: baclofen | MAS at 12 weeks was significantly lower in the treatment group (1.77 vs. 2.24, P=0.03). | NR | Mean GMFMd at 12 weeks was significantly higher in the treatment group (74.45 vs. 68.23, P<0.001). | Tizanidine: better safety profile than baclofen, exact values not provided |
| - In both groups, increases in GMFM from baseline were significant (P<0.001 for both). | Baclofen: higher incidence of anorexia and abdominal pain | |||
| Nikkhah et al. (2011) [15] Control: placebo | A higher proportion of patients with reduced spasticity was found in the treatment group relative to the control (50% vs. 6.7%, P<0.0001). | Higher proportion of pain reduction in spastic extremities in treatment than control group (66.7% vs. 13.3%, P<0.0001) | NR | No serious side effects were reported. |
| Dai et al. (2016) [12]b Control: baclofen | MAS at 12 weeks exhibited no significant difference between groups (1.94 vs. 2.68, P=0.596). | NR | Mean GMFMd at 12 weeks was significantly higher in the treatment group (76.63 vs. 68.17, P<0.001). | Both groups: constipation, anorexia, lethargy, and fatigue, but suppressed with botulinum toxin A |
| - In the treatment group, the decline of MAS from baseline to week 12 was significant (3.79 vs. 1.94, P=0.048); however, it was not significant in the control group. | - In both groups, the increase in GMFM from baseline was significant (P<0.001 for both). | Baclofen: seizure and nasal congestion | ||
| Haque et al. (2020) [16]c Control: baclofen | Faster MAS score reduction was observed in the treatment group. | NR | Utilized GMF Classification Scalee. After 6 mo, most patients in the treatment group were levels 2 and 3 (76%), while >50% in control group were level 4. | Adverse events were higher in the baclofen group vs. the treatment group, but no other details were provided. |
| At the end of month 6, those with MAS score 1 constituted 46% of the treatment group vs. <20% in the control group. |
MAS, modified Ashworth scale; NR, not reported; GMFM, Gross Motor Functional Measurement; GMF, Gross Motor Function.
aAll patients underwent rehabilitation; bAll patients received rehabilitation and local injections of botulinum toxin A; cAll patients underwent supervised physiotherapy; dIn GMFM, higher scores denote a greater improvement in gross motor function; eIn the GMF Classification Scale, a higher level denotes a more severe limitation in mobility.
References
- TOOLS
-
METRICS

-
- 0 Crossref
- Scopus
- 2,627 View
- 73 Download
- Related articles in Ann Child Neurol
-
Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Indonesian Patients with Cerebral Palsy2023 October;31(4)
Risk Factors for Chronic Kidney Disease in Pediatric Patients with Epilepsy2021 January;29(1)